\n",
"int main() {\n",
" double n = -0.1;\n",
" long int* ni = (long int *) &n;\n",
" \n",
" printf(\"%ld\\n\", sizeof(n));\n",
" printf(\"%ld\\n\", sizeof(*ni));\n",
" printf(\"%016x\\n\", *ni);\n",
"}"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"!gcc floatbinary.c -o floatbinary && ./floatbinary"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"deletable": false,
"nbgrader": {
"cell_type": "markdown",
"checksum": "10cffbb806f50f9efce3b5cb4cf7e7ff",
"grade": true,
"grade_id": "cell-6c7b64b4e6a14cc1",
"locked": false,
"points": 20,
"schema_version": 3,
"solution": true,
"task": false
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
},
"tags": []
},
"source": [
"YOUR ANSWER HERE"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "r2A9ApyaL9fB",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"##### Differences from C\n",
"Note that unlike many languages, **Python does not have unary increment** (x++) or decrement (x--) operators.\n",
"\n",
"Python also has built-in types for complex numbers; you can find all of the details in the [Builtin types documentation](https://docs.python.org/3.8/library/stdtypes.html#numeric-types-int-float-long-complex)."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "Nv_LIVOJL9fD",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"#### Booleans\n",
"\n",
"Python implements all of the usual operators for Boolean logic, but uses English words rather than symbols (`&&`, `||`, etc.):"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "RvoImwgGL9fE",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"t = True; f = False\n",
"print(type(t))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "YQgmQfOgL9fI",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"Now we let's look at the operations:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "6zYm7WzCL9fK",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(t and f) # Logical AND;\n",
"print(t or f) # Logical OR;\n",
"print(not t) # Logical NOT;\n",
"print(t != f) # Logical XOR;"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"#### NoneType\n",
"`None` constant can be thought of has `nullptr` in C. It has its own type `NoneType`."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"n = None\n",
"type(None), type(n)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "UQnQWFEyL9fP",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"### Sequences\n",
"\n",
"* **str** (strings): usually to represent text. However, anything that is wrapped in quotes (single or double) is treated as a string.\n",
"* **list** (lists): Like a C array, more like C++ std::vector. Dynamically allocated and memory managed.\n",
"* **tuple** : Like lists but immutable.\n",
"* **set**: Like lists, mutable. Checks for uniqueness of each value.\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"#### Strings"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "AijEDtPFL9fP",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"hello = 'he\"llo' # String literals can use single quotes\n",
"world = \"world'\" # or double quotes; it does not matter\n",
"great = \"\"\"Python\n",
"also has triple quotes\n",
"which can internally contain \n",
"newlines, 'single quotes' and \"double quotes\". \n",
"Triple quotes are often used for documentation\n",
"and multi-line comments.\n",
"\"\"\"\n",
"print(hello)\n",
"print(len(hello))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "saDeaA7hL9fT",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"hw = hello + ', ' + world # String concatenation\n",
"print(hw)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "Nji1_UjYL9fY",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"num = 12\n",
"hw12 = f'{hello:s} {world} {num:d}' # string formatting\n",
"hw12"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"\"First, thou shalt count to {0}\" # References first positional argument\n",
"\"Bring me a {}\" # Implicitly references the first positional argument\n",
"\"From {} to {}\" # Same as \"From {0} to {1}\"\n",
"\"My quest is {name}\" # References keyword argument 'name'\n",
"\"Weight in tons {0.weight}\" # 'weight' attribute of first positional arg\n",
"\"Units destroyed: {players[0]}\" # First element of keyword argument 'players'."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "oMUHQqm6XR27",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"String formatting has its [own mini language](https://docs.python.org/3.8/library/string.html#formatspec).\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"format_spec ::= [[fill]align][sign][#][0][width][grouping_option][.precision][type]\n",
"fill ::= <any character>\n",
"align ::= "<" | ">" | "=" | "^"\n",
"sign ::= "+" | "-" | " "\n",
"width ::= digit+\n",
"grouping_option ::= "_" | ","\n",
"precision ::= digit+\n",
"type ::= "b" | "c" | "d" | "e" | "E" | "f" | "F" | "g" | "G" | "n" | "o" | "s" | "x" | "X" | "%"\n",
""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "a7DAK5bmWtgP",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"hw12 = '%s %s %d' % (hello, world, 12) # C-style string formatting using % operator\n",
"hw12"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "Ll6wRsO4ZS1h",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"Since Python 3.8, the dominant way to format strings is to use [f-string](https://docs.python.org/3/glossary.html#term-f-string)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "38_U-Hg7YxMI",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"hello = \"Hell'o\"\n",
"world = 'World\"'\n",
"i = 12\n",
"hw12 = F'{hello:s} {world} {i:d}'# string formatting using f-strings\n",
"hw12"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "BN6Ka_cyacaL",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"hw12 = hello + world + str(12)\n",
"print(hw12)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "vFqZ-fFC_KxZ",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"hw12 = hello + ' ' + world + ' ' + str(3.1415)\n",
"print(hw12)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "4tjJcT_eaFOm",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Yes you can use emojis (unicode support)\n",
"f\"{hello} 😀 😃 😄 😁 😆 {i:d} emojies\""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "CsJzWurrahjk",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"Or you can use [Unicode names for emojies](https://docs.python.org/3/howto/unicode.html)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "W8gBwi4Eatm6",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"\"\\N{GRINNING FACE}\""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "bUpl35bIL9fc",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"String objects have a bunch of useful methods; for example:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "VOxGatlsL9fd",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"s = \"hello\"\n",
"print(s.capitalize()) # Capitalize a string\n",
"print(s.upper()) # Convert a string to uppercase; prints \"HELLO\"\n",
"print(s.rjust(7)) # Right-justify a string, padding with spaces\n",
"print(s.center(7)) # Center a string, padding with spaces\n",
"print(s.replace('l', '(ell)')) # Replace all instances of one substring with another"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "3TPiIvkN_z98",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"s = 'hello'\n",
"s = s.upper()\n",
"print(s)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "vF00P7btXiSO",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"You can ask for help on any python function, object or type using \"?\""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "wm6gBA0BXffY",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
" # a jupyter notebook feature, not python\n",
"s.upper?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "6DASciYCX4DQ",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"help(s.upper) # Some as s.upper? but a python feature"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "Hpy-ZDCZYJPk",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"dir(s) # List all the functions available on a string object"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "CRT0QMj3PbGj",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"**Whitespace**: any nonprinting character, such as spaces, tabs, and end-of-line symbols"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "WowvLGAfPqW6",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(\"ECE 491/591\\n\\tDeep Learning\\nis fun!\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "xy-5QHb2PZx_",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(' w\\to\\tr l\\nd '.strip()) # Strip leading and trailing whitespace"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "zkohEUdQQL2w",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(' world '.rstrip()) # Strip trailing whitespace"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "fdxUM68hQie0",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(' world '.lstrip()) # Strip leading whitespace"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "06cayXLtL9fi",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"You can find a list of all string methods in the [documentation](https://docs.python.org/3.7/library/stdtypes.html#string-methods)."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "S3tkgmsvBKd9",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"#### Difference from C\n",
"C is statically typed vs Python is dynamically typed. You can change the type of a variable from one line to another."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "Bpgx2b-c-63n",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"x = 1\n",
"print(\"1. Type of x = \", type(x))\n",
"x = \"str\"\n",
"print(\"2. Type of x = \", type(x))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "UsIWOe0LL9fn",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"#### Lists"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "wzxX7rgWL9fn",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"source": [
"A list is the Python equivalent of an array, but is resizeable and can contain elements of different types:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "QmHcwNjubev4",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"lst = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]\n",
"print(lst)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "YMnnw-K-coqI",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"**Index Positions Start at 0, Not 1**"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "dvdKRR5Sb15z",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"lst[0]"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "hk3A8pPcL9fp",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"xs = [1, 2, 3, 'hello', [4, 5, 6]] # Create a list\n",
"print(xs)\n",
"print('First element of the array: ', xs[0]) # Index to the list starts with 0\n",
"print('Last element of the array: ', xs[4])\n",
"print(xs[4][1])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "u-SeyJugSnXm",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Negative indices count from the end of the list; \n",
"print(xs[-1]) # Index -1 returns the last item in the list\n",
"print(xs[-2]) # Index -2 returns the second item from the end of the list"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "YCjCy_0_L9ft",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"xs[2] = 'foo' # Lists can contain elements of different types\n",
"print(xs) "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "vJ0x5cF-L9fx",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"xs.append('bar') # Add a new element to the end of the list\n",
"print(xs) "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "cxVCNRTNL9f1",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(xs)\n",
"x = xs.pop() # Remove and return the last element of the list\n",
"print(x)\n",
"print(xs)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "Kq5WHOEzTKYm",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"xs.insert(1, \"new item\") # Insert the \"new item\" at the index 1\n",
"print(xs) "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "rUZ2UU1MTx_y",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"xs.remove(\"foo\") # Removing an item by value\n",
"print(xs)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "ilyoyO34L9f4",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"As usual, you can find all the details about lists in the [documentation](https://docs.python.org/3.8/tutorial/datastructures.html#more-on-lists).\n",
"\n",
"Exercise 4: Read the the documentation to find out whether Python lists are implemented as array datastructure or linked list datastructure."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"deletable": false,
"nbgrader": {
"cell_type": "markdown",
"checksum": "8103634c4b482c1aa15d003063f0d803",
"grade": true,
"grade_id": "cell-899d7f310f010b33",
"locked": false,
"points": 10,
"schema_version": 3,
"solution": true,
"task": false
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
},
"tags": []
},
"source": [
"YOUR ANSWER HERE"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "0UN6AzpaB-yp",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"colors = [\"Red\", \"Green\", \"White\", \"Black\"]\n",
"# Print the first color in the above list\n",
"print(colors[0])\n",
"# Print the last color in the above list\n",
"print(colors[-1])\n",
"# Append \"Blue\" to the above list\n",
"colors.append('Blue')\n",
"print(colors)\n",
"# Remove \"Green\" from the above list\n",
"colors.remove('Green')\n",
"print(colors)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "4qR6pXLXe2uh",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"source": [
"Exercise 5: Find the length of the list `colors`. "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"deletable": false,
"id": "TLACKBuUe92y",
"nbgrader": {
"cell_type": "code",
"checksum": "15e81c33179fd07bcc602ce458d35999",
"grade": false,
"grade_id": "cell-711b6cbf20d544c0",
"locked": false,
"schema_version": 3,
"solution": true,
"task": false
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
},
"tags": []
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# YOUR CODE HERE\n",
"raise NotImplementedError()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"deletable": false,
"editable": false,
"nbgrader": {
"cell_type": "code",
"checksum": "f6cdb3c8723657e22245b94cc8bfd859",
"grade": true,
"grade_id": "cell-08d951a4a5fb5045",
"locked": true,
"points": 5,
"schema_version": 3,
"solution": false,
"task": false
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
},
"tags": []
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Last cell should output length of the list `colors`"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "vwbt_pirA6Gv",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
" In-class Excercises 6: What is the difference between sorted(colors) and colors.sort()? "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "OC9qQkgOfi7g",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"colors = [\"Red\", \"Green\", \"White\", \"Black\"]\n",
"colors2 = sorted(colors)\n",
"colors2, colors"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "VkaIRgQKBOg9",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"colors.sort()\n",
"colors"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"deletable": false,
"nbgrader": {
"cell_type": "markdown",
"checksum": "2c47bbefefb9e58e45c80c380096c6d0",
"grade": true,
"grade_id": "cell-961cc4c9eaed10f6",
"locked": false,
"points": 5,
"schema_version": 3,
"solution": true,
"task": false
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
},
"tags": []
},
"source": [
"YOUR ANSWER HERE"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "ovahhxd_L9f5",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"#### Slicing"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "YeSYKhv9L9f6",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"source": [
"In addition to accessing list elements one at a time, Python provides concise syntax to access sublists; this is known as slicing:\n",
"\n",
"* aList[**start:stop:step**]\n",
"* aList[**start:stop**]\n",
"\n",
"The default for **start** is none or 0. \n",
"\n",
"The default **stop** is the end of your data structure. \n",
"\n",
"Using a positive number references from the first element, a negative number references from last element in your structure."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "ninq666bL9f6",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# nums = range(5) # Python 2, but error in Python 3\n",
"nums = list(range(5)) # range is a built-in function that creates a list of integers\n",
"nums = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]\n",
"print(nums) # Prints \"[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]\"\n",
"print(nums[2:4]) # Get a slice from index 2 to 4 (exclusive); prints \"[2, 3]\"\n",
"print(nums[2:]) # Get a slice from index 2 to the end; prints \"[2, 3, 4]\"\n",
"print(nums[:2]) # Get a slice from the start to index 2 (exclusive); prints \"[0, 1]\"\n",
"print(nums[:]) # Get a slice of the whole list; prints [\"0, 1, 2, 3, 4]\"\n",
"print(nums[::-1]) # Slice indices can be negative; prints [\"0, 1, 2, 3]\"\n",
"nums[2:4] = [8, 9] # Assign a new sublist to a slice\n",
"print(nums) # Prints \"[0, 1, 8, 9, 4]\""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "4N1ao1fbC6gs",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"lst = list(range(0,100,10))\n",
"print(lst)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "UmOA19VODKnO",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Print everything except the last three elements\n",
"print(lst[:-3])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "u3R02qZaDPHu",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Print everything with odd indices\n",
"print(lst[::2])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "0aEcIpN5D6gs",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Print everything with even indices\n",
"print(lst[1::2])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "3cv_b7esEDkH",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Print everything in reversed order\n",
"print(lst[::-1])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "4RRJ3mEvCmUK",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
" In-class Excercises 7: Select 6th,5th, and 4th element from the following list `A`. "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "l_gYn32_hccI",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"A = list(range(1,10,1)) # start,stop,step\n",
"print(A)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"deletable": false,
"id": "mzbPvkFzjWMl",
"nbgrader": {
"cell_type": "code",
"checksum": "d4624a0a94e655f38a86f291b381cf14",
"grade": false,
"grade_id": "cell-11e1de3272672679",
"locked": false,
"schema_version": 3,
"solution": true,
"task": false
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
},
"tags": []
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# YOUR CODE HERE\n",
"raise NotImplementedError()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"deletable": false,
"editable": false,
"nbgrader": {
"cell_type": "code",
"checksum": "261123a94a46d06185310a9923673855",
"grade": true,
"grade_id": "cell-77ef2501dad25981",
"locked": true,
"points": 5,
"schema_version": 3,
"solution": false,
"task": false
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
},
"tags": []
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Last cell should output length of the list `colors`"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "UONpMhF4L9f_",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"#### Loops"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "_DYz1j6QL9f_",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"source": [
"You can loop over the elements of a list like this:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "4cCOysfWL9gA",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"animals = ['cat', 'dog', 'monkey']\n",
"for animal in animals:\n",
" print(animal)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"You can print squares of first 20 numbers like this:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"for i in range(1, 21):\n",
" print(f\"{i:d}^2 = {i*i:d}\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "KxIaQs7pL9gE",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"##### Differences from C\n",
"Unlike C there are no braces for start and end of the for loop. Instead of braces, we have a compbination of \":\" colon and indentation. Unlike C, indentation is mandatory in Python.\n",
"\n",
"If you want access to the index of each element within the body of a loop, use the built-in `enumerate` function:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "JjGnDluWL9gF",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"animals = ['cat', 'dog', 'monkey']\n",
"for idx, animal in enumerate(animals):\n",
" print('#{}: {}'.format(idx, animal))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"##### Exercise 9\n",
"\n",
"Write code to create a list of 20 elements of fibonacci series: $f_0 = 0$, $f_1 = 1$, and $f_n = f_{n-1} + f_{n-2}$ for all $n \\ge 2$. Assign the list to variable called FIB20.\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": []
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"deletable": false,
"nbgrader": {
"cell_type": "code",
"checksum": "454b6f27a3b14d728dcbe6213ce76eb6",
"grade": false,
"grade_id": "cell-a524476b59e11486",
"locked": false,
"schema_version": 3,
"solution": true,
"task": false
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
},
"tags": []
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# YOUR CODE HERE\n",
"raise NotImplementedError()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"deletable": false,
"editable": false,
"nbgrader": {
"cell_type": "code",
"checksum": "3866d385712294577175e765647d07cb",
"grade": true,
"grade_id": "cell-29cf37a9b9e5da65",
"locked": true,
"points": 20,
"schema_version": 3,
"solution": false,
"task": false
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
},
"tags": []
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"assert len(FIB20) == 20\n",
"assert FIB20[0] == 0\n",
"assert FIB20[1] == 1\n",
"### START HIDDEN TESTS\n",
"assert FIB20 == [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, 377, 610, 987, 1597, 2584, 4181]"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "7761hhtzeIrJ",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"#### Copying a list"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "X4iruzPrfOWR",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"To copy a list, you can make a slice that includes the entire original list\n",
"by omitting the first index and the second index ([:]). This tells Python to\n",
"make a slice that starts at the first item and ends with the last item, producing\n",
"a copy of the entire list."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "NH6ayWFdeHYU",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]\n",
"b = a[:] # copying the list\n",
"# b = a.copy() # <- preferred way\n",
"c = a # This doesn't copy the list!\n",
"\n",
"a.append('x') # a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 'x']\n",
"b.append('y') # b = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 'y']\n",
"c.append('z') # c = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 'x', 'z']\n",
"\n",
"print('a = ', a)\n",
"print('b = ', b)\n",
"print('c = ', c)\n",
"print('a = ', a)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "arrLCcMyL9gK",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"#### List comprehensions:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "5Qn2jU_pL9gL",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"source": [
"When programming, frequently we want to transform one type of data into another. As a simple example, consider the following code that computes square numbers:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "IVNEwoMXL9gL",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"nums = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]\n",
"squares = []\n",
"for x in nums: # Don't forget the colon\n",
" squares.append(x ** 2)\n",
"print(squares)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "7DmKVUFaL9gQ",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"source": [
"You can make this code simpler using a list comprehension:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "kZxsUfV6L9gR",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"nums = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]\n",
"squares = [x ** 2 for x in nums]\n",
"print(squares)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "-D8ARK7tL9gV",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"List comprehensions can also contain conditions:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "yUtgOyyYL9gV",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"nums = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]\n",
"even_squares = [x ** 2 for x in nums if (x % 2 == 0 and x <=2)]\n",
"print(even_squares)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "H8xsUEFpL9gZ",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"#### Dictionaries"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "kkjAGMAJL9ga",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"source": [
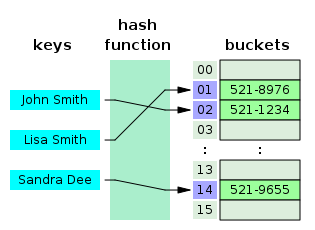
"A dictionary stores (key, value) pairs, similar to a `Map` in Java or an object in Javascript. It is implemented as a [hash table](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hash_table). \n",
"\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"You can use it like this:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "XBYI1MrYL9gb",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"d = {'cat': 'cute', 'dog': 'furry'} # Create a new dictionary with some data\n",
"print(d['cat']) # Get an entry from a dictionary; prints \"cute\"\n",
"key = 'cat'\n",
"print(d[key])\n",
"print('cat' in d) # Check if a dictionary has a given key; prints \"True\""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "4_bPWZAfhwLv",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"Adding a new key-value pair"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "pS7e-G-HL9gf",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"d['fish'] = 'wet' # Set an entry in a dictionary\n",
"print(d['fish']) # Prints \"wet\"\n",
"\n",
"d['elephant'] = 'heavy' # Set an entry in a dictionary\n",
"print(d['elephant']) # Prints \"heavy\""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "zy1_tEtqj0Rv",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"Looping through a dictionary"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "yngQ8bQfj3sQ",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"for key, value in d.items():\n",
" print('key = ', key, '\\t value = ', value)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "gMynGQKEkcn_",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"for key in d.keys():\n",
" print('key = ', key, '\\tvalue = ', d[key])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "oU6QMrO-k2B0",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"for key in sorted(d.keys()): # sorting the key\n",
" print('key = ', key, '\\t\\tvalue = ', d[key])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "hwnFSEeTlbK-",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"for value in sorted(d.values()): # print all values\n",
" print('value = ', value)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "tFY065ItL9gi",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print('monkey' in d)\n",
"\n",
"# print(d['monkey']) # KeyError: 'monkey' not a key of d"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "AV3EoVzejUj2",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"For dictionaries, we can use the get() method to set a default value that will be returned if the requested key doesn’t exist."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "8TjbEWqML9gl",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(d.get('monkey', 'N/A')) # Get an element with a default; prints \"N/A\"\n",
"print(d.get('fish', 'N/A')) # Get an element with a default; prints \"wet\""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "Nk2wF6aRiG1X",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"Removing a key-value pair"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "0EItdNBJL9go",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"del d['fish'] # Remove an element from a dictionary\n",
"\n",
"# Be aware that the deleted key-value pair is removed permanently.\n",
"print(d.get('fish', 'N/A')) # \"fish\" is no longer a key; prints \"N/A\""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "wqm4dRZNL9gr",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"source": [
"You can find all you need to know about dictionaries in the [documentation](https://docs.python.org/2/library/stdtypes.html#dict)."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "IxwEqHlGL9gr"
},
"source": [
"It is easy to iterate over the keys in a dictionary:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "rYfz7ZKNL9gs"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"d = {'person': 2, 'cat': 4, 'spider': 8}\n",
"for animal, legs in d.items():\n",
" print('A {} has {} legs'.format(animal, legs))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "17sxiOpzL9gz"
},
"source": [
"Dictionary comprehensions: These are similar to list comprehensions, but allow you to easily construct dictionaries. For example:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "8PB07imLL9gz",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"nums = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]\n",
"even_num_to_square = {x: x ** 2 for x in nums if x % 2 == 0}\n",
"print(even_num_to_square)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "qPsHSKB1L9hF",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"#### Tuples"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "kucc0LKVL9hG",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"source": [
"A tuple is an (immutable) ordered list of values. Python refers to values that cannot change as immutable, and an immutable list is called a tuple."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "0R0xAUTigZ7f",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"dimensions = (800, 600)\n",
"print(dimensions[0])\n",
"print(dimensions[1])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "RTCP4icsCN-N",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"source": [
"Note that comma creates a tuple not parantheses. Always use parantheses to increase readability."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "rbMZWkk7CUEk"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"dimensions = 800, 600\n",
"print(dimensions[0])\n",
"print(dimensions[1])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "3E_SuJaGgnvg"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Try this (uncomment)\n",
"# dimensions[0] = 1000 # this will return error "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "x7Dem8CxgZEz"
},
"source": [
"A tuple is in many ways similar to a list; one of the most important differences is that tuples can be used as keys in dictionaries and as elements of sets, while lists cannot. Here is a trivial example:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "9wHUyTKxL9hH"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"d = {(x, x + 1): x for x in range(10)} # Create a dictionary with tuple keys\n",
"t = (5, 6) # Create a tuple\n",
"print(type(t))\n",
"print(d[t]) \n",
"print(d[(1, 2)])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "gHw9hjSgClmz",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"Any sequence (list, tuple, set) can be _unpacked_ into individual variables."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "3s_OArLXRo0P",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"dimensionx, dimensiony = dimensions"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "5XKKRCGsDPk6",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"x, y, z = [1, 2, 3] # Lists can be used for Multiple assignment \n",
"print(x, y, z)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "O_Aak5bADf5Q",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"x, y, *rest = range(10) # Lists can be used for Multiple assignment \n",
"x, y, rest"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "azrHHC0-DH4t",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"x, y, z = 1, 2, 3 # Tuples can be used for Multiple assignment \n",
"print(x, y, z)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "K9f25_1jlNRF",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"### Flow Control"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "a2EwpTgQmayj",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"fruits = [\"apple\", \"banana\", \"cherry\"]\n",
"for x in fruits:\n",
" print(x)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "vt5SHmnzmgPR",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"for x in \"banana\": # string is also a sequence type\n",
" print(x)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "rzJWiU0jmj3c",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"fruits = [\"apple\", \"banana\", \"cherry\"]\n",
"for x in fruits:\n",
" if x == \"banana\":\n",
" break\n",
" print(x) "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "9gbZ7NtLmpMd",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"fruits = [\"apple\", \"banana\", \"cherry\"]\n",
"for x in fruits:\n",
" if x == \"banana\":\n",
" continue\n",
" print(x)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "UXfW14pKc_Ab",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Shows while loop. Do not use this style though, prefer for loop. \n",
"# This style is considered not Pythonic\n",
"# https://peps.python.org/pep-0008/\n",
"idx = 0\n",
"while (idx < len(fruits)):\n",
" print(fruits[idx])\n",
" idx += 1"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "CXMuxRe2ldUK",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"age = 19\n",
"if age >= 18:\n",
" print(\"You are old enough to vote!\")\n",
"else:\n",
" print(\"Sorry, you are too young to vote.\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "K_cH-E6sl02v",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"age = 12\n",
"if age < 4:\n",
" price = 0\n",
"elif age < 18:\n",
" price = 25\n",
"else:\n",
" price = 40\n",
"\n",
"print(f\"Your admission cost is ${price}.\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "1ASYoQRycx2T",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"### Differences from C\n",
"\n",
"There is no `do {} while()` in Python. "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"source": [
"#### Truth value testing\n",
"\n",
"Any objects can be tested for truth value in `if` and `while` statements. Most objects are considered true, except the following ones which are considered false:\n",
"\n",
"* constants defined to be false: None and False.\n",
"\n",
"* zero of any numeric type: 0, 0.0, 0j, Decimal(0), Fraction(0, 1)\n",
"\n",
"* empty sequences and collections: '', (), [], {}, set(), range(0)\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "AXA4jrEOL9hM",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"### Functions"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "WaRms-QfL9hN",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"source": [
"Python functions are defined using the `def` keyword. For example:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "RkuRguV-jvP5",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Making the argument b and c optional with 4 and 8 as default values\n",
"def sum2(a, b=4, c=8): \n",
" return a + b + c, a*b*c # Returns a tuple of two values"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "Bbsc-8Ivj3bY",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"sum2(1, c=5)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "pKf2_UzqkwNa",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"sum_, prod_ = sum2(1, c=5) # Unpacking a tuple"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "oZE6AoRvk77-",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"prod_"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "kiMDUr58L9hN",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"def sign(x, y=100):\n",
" if x > 0:\n",
" return 'positive', 123\n",
" elif x < 0:\n",
" return 'negative', 123\n",
" else:\n",
" return 'zero', 123\n",
"\n",
"for x in [-1, 0, 1]:\n",
" v1, _ = sign(x)\n",
" print(v1)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "U-QJFt8TL9hR",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"We will often define functions to take [optional keyword](https://docs.python.org/3/glossary.html#term-keyword-argument) arguments, like this:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "PfsZ3DazL9hR",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"def hello(name, loud=False):\n",
" if loud:\n",
" print('HELLO, {}'.format(name.upper()))\n",
" else:\n",
" print('Hello, {}!'.format(name))\n",
"\n",
"hello('Bob')\n",
"hello('Fred', loud=True)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "kHknme7EocwW",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"Modifing a list in a function\n",
"\n",
"When you pass a list to a function, the function can modify the list."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "CdIUyKhMobjw",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"def fun(list):\n",
" list.append('new item')\n",
"\n",
"a = [1, 2, 3]\n",
"fun(a)\n",
"print(a)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "KZOZ7eKXpH5b",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"If you want to prevent a function from modifying a list, you can send a copy of a list to the function"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "7aT96a74pY6X",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"def fun(lst):\n",
" lst.append('new item')\n",
"\n",
"a = [1, 2, 3]\n",
"# Preventing a Function from Modifying a List\n",
"fun(a[:]) # The slice notation [:] makes a copy of the list\n",
"# fun(a.copy()) \n",
"print(a)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "eHzBWi4UGJIq",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"** In-class Excercises 8**"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "4mmpsHIfGKJY",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Write a function named \"first_last\" that returns a list that contains only the first and the last element of a given list \n",
"def first_last(a):\n",
" return a[0::len(a)-1]\n",
"\n",
"first_last([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])\n",
"\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "baqShM2N8UWM",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"### Variable Scope \n",
"\n",
"The LEGB scope lookup rule. When a variable is referenced, Python searches for it in\n",
"this order: in the local scope, in any enclosing functions’ local scopes, in the global scope, and finally\n",
"in the built-in scope. The first occurrence wins. The place in your code where a variable is assigned\n",
"usually determines its scope. In Python 3, nonlocal declarations can also force names to be mapped\n",
"to enclosing function scopes, whether assigned or not."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "hXRCy21T9RN-",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"source": [
""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "NLlLovU78W2Q",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Global scope\n",
"X = 99 # X and func assigned in module: global\n",
"\n",
"def func(Y): # Y and Z assigned in function: locals\n",
" # Local scope\n",
" Z = X + Y # X is a global\n",
" return Z\n",
"\n",
"func(1) # func in module: result=100"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "RVZwE1-r91kH",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"X = 99 # Global scope name: not used\n",
"\n",
"def f1():\n",
" X = 88 # Enclosing def local\n",
" def f2():\n",
" print(X) # Reference made in nested def\n",
" f2()\n",
"\n",
"f1() # Prints 88: enclosing def local\n",
"print(X)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "YO1urliO8iE6",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"X = 99 # Global X\n",
"\n",
"def func():\n",
" X = 88 # Local X: hides global\n",
"\n",
"func()\n",
"print(X) # Prints Global X 99: unchanged"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "ryS19k3x8zjF",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"The assignment within the function creates a local X that is a completely different\n",
"variable from the global X in the module outside the function."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "A3r-ho9z85rQ",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"X = 99 # Global X\n",
"\n",
"def func():\n",
" global X\n",
" X = 88 # Local X: overrides global\n",
"\n",
"func()\n",
"print(X) # Prints 88: unchanged"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"for x in range(100):\n",
" pass\n",
"\n",
"# what is x\n",
"x"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"x = 0\n",
"for i in range(100):\n",
" if i % 23 == 0:\n",
" x = 23\n",
" else:\n",
" x = 1\n",
"# what is x?\n",
"x"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"x = 0\n",
"def foo():\n",
" for i in range(100):\n",
" if i % 23 == 0:\n",
" x = 23\n",
" else:\n",
" x = 1\n",
"# what is x?\n",
"x"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"### Exercise : Implement a sqrt function\n",
"\n",
"As a way to play with functions and loops, let’s implement a square root function: given a number x, we want to find the number z for which z² is most nearly x.\n",
"\n",
"Computers typically compute the square root of x using a loop. Starting with some guess z, we can adjust z based on how close z² is to x, producing a better guess:\n",
"$z' = z - (z^2 - x) / (2z) $\n",
"\n",
"Repeating this adjustment makes the guess better and better until we reach an answer that is as close to the actual square root as can be.\n",
"\n",
"Implement this in the def sqrt provided. A decent starting guess for z is 1, no matter what the input. To begin with, repeat the calculation 10 times and print each z along the way. See how close you get to the answer for various values of x (1, 2, 3, …) and how quickly the guess improves.\n",
"\n",
"Next, change the loop condition to stop once the value has stopped changing (or only changes by a very small amount). See if that’s more or fewer than 10 iterations. Try other initial guesses for z, like x, or x/2. How close are your function’s results to the math.sqrt in the standard library?\n",
"\n",
"(Note: If you are interested in the details of the algorithm, the z² − x above is how far away z² is from where it needs to be (x), and the division by 2z is the derivative of z², to scale how much we adjust z by how quickly z² is changing. This general approach is called Newton’s method. It works well for many functions but especially well for square root. Newton’s methods is particular form of gradient descent.)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"deletable": false,
"nbgrader": {
"cell_type": "code",
"checksum": "8fb1d90a265589f45eed07cf742bba6b",
"grade": false,
"grade_id": "cell-30c08b69b69ff8c1",
"locked": false,
"schema_version": 3,
"solution": true,
"task": false
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
},
"tags": []
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"def sqrt(x):\n",
" assert x >= 0 # throws an error if x is negative\n",
" # YOUR CODE HERE\n",
" raise NotImplementedError()\n",
" \n",
"sqrt(2)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"deletable": false,
"editable": false,
"nbgrader": {
"cell_type": "code",
"checksum": "fc015efafb9c9e9bc6cdc7dd8f046e86",
"grade": true,
"grade_id": "cell-aaacc93f0f82ee73",
"locked": true,
"points": 20,
"schema_version": 3,
"solution": false,
"task": false
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
},
"tags": []
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"x = 2; z = sqrt(x)\n",
"assert abs(z*z - x) < 1e-8\n",
"x = 3; z = sqrt(x)\n",
"assert abs(z*z - x) < 1e-8\n",
"x = 4; z = sqrt(x)\n",
"assert abs(z*z - x) < 1e-8\n",
"import random\n",
"for _ in range(10):\n",
" x = random.randint(1, 100); z = sqrt(x)\n",
" assert abs(z*z - x) < 1e-6\n",
"'success'"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "ZKEfJ3e78ANJ",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"### Asterisks in Python"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "M7hIUZyN8CE_",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"3 * 5"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "9xoOh5PL8FB9",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"3 ** 5"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "_q6Xl8NJ8HA_",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Using * to unpack iterables into a list/tuple\n",
"numbers = [2, 1, 3, 4, 7]\n",
"more_numbers = [*numbers, 11, 18]\n",
"print(*more_numbers, sep=', ')\n",
"\n",
"first, *rest = [*numbers, 11, 18]\n",
"print(rest, sep=', ')"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "ZHh2C4uH9TDl",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Unpack a dictionary\n",
"date_info = {'year': \"2020\", 'month': \"01\", 'day': \"01\"}\n",
"filename = \"{year}-{month}-{day}.txt\".format(**date_info)\n",
"print(filename)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "XN_p33qL97B9",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"### zip"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "0xrey4AK-CNJ",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"source": [
"The zip() function takes iterables (can be zero or more), aggregates them in a tuple, and returns it."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "vv1tawNe98k3",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"languages = ['Java', 'Python', 'JavaScript']\n",
"versions = [14, 3, 6]\n",
"\n",
"result = list(zip(languages, versions))\n",
"print(result)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"`zip` is almost the inverse of itself. It result in the same lists that you started with. "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"list(zip(*result))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"mat = [[1, 2, 3],\n",
" [4, 5, 6]]\n",
"mat_transpose = list(zip(*mat))\n",
"print(mat_transpose)\n",
"print(list(zip(*mat_transpose)))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "Y0paQcOzAf6E",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"for (x, y) in zip(languages, versions): # pairs of items pulled from two lists\n",
" print(x, y)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "cD5QKJ3rBVn5",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"keys = ['spam', 'eggs', 'toast']\n",
"vals = [1, 3, 5]\n",
"\n",
"D2 = {}\n",
"for (k, v) in zip(keys, vals): \n",
" D2[k] = v\n",
"\n",
"D2"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "hJL1tFuoBH3N",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"zip function is more general than this example suggests. For instance,\n",
"it accepts any type of sequence (really, any iterable object, including files), and\n",
"it accepts more than two arguments. With three arguments, as in the following example,\n",
"it builds a list of three-item tuples with items from each sequence, essentially projecting\n",
"by columns (technically, we get an N-ary tuple for N arguments):"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "igHuGfuVA4cF"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"T1, T2, T3 = (1,2,3), (4,5,6), (7,8,9)\n",
"list(zip(T1, T2, T3))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "6HQY3GPU-S3H"
},
"source": [
"The * operator can be used in conjunction with zip() to unzip the list."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "miGfL6H1-TZp"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"coordinate = ['x', 'y', 'z']\n",
"value = [3, 4, 5]\n",
"\n",
"result = zip(coordinate, value)\n",
"result_list = list(result)\n",
"print(result_list)\n",
"\n",
"c, v = zip(*result_list)\n",
"print('c =', c)\n",
"print('v =', v)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "ObA9PRtQL9hT",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"### Classes"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "hAzL_lTkL9hU",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"source": [
"#### Defining a Class\n",
"\n",
"The syntax for defining classes in Python is :"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "F0xt8IhX0DN8",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"class Addition: \n",
" # first = 0\n",
" # second = 0\n",
" answer = 0 # Class member\n",
" \n",
" # parameterized constructor \n",
" def __init__(self, first, second): \n",
" self.first = first \n",
" self.second = second \n",
"\n",
" def display(self): \n",
" print(\"First number = \" + str(self.first)) \n",
" print(\"Second number = \" + str(self.second)) \n",
" print(\"Addition of two numbers = \" + str(self.answer)) \n",
"\n",
" def calculate(self): \n",
" self.answer = self.first + self.second \n",
" \n",
"# creating object of the class \n",
"# this will invoke parameterized constructor \n",
"obj = Addition(1000, 2000) \n",
"\n",
"# perform Addition \n",
"obj.calculate() \n",
"\n",
"# display result \n",
"obj.display() \n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "RWdbaGigL9hU",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"class Person:\n",
"\n",
" # Constructor\n",
" def __init__(self, name):\n",
" self.name = name # Create an instance variable\n",
"\n",
" # Instance method\n",
" def getName(self):\n",
" return self.name \n",
"\n",
" # To check if this person is an employee \n",
" def isEmployee(self): \n",
" return False\n",
"\n",
"# Making an instance from a class\n",
"g = Person('Fred') # Construct an instance of the Greeter class\n",
"\n",
"# Accessing attributes\n",
"print(g.name)\n",
"\n",
"# Calling methods\n",
"print(g.getName()) "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "dqdK--1VtSo8",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"* The **self** parameter is required in the method definition, and it must come first before the other parameters. It must be included in the definition because when Python calls this method later (to create an instance), the method call will automatically pass the self argument.\n",
"* Every method call associated with an instance automatically passes **self**, which is a reference to the instance itself; it gives the individual instance access to the attributes and methods in the class."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "8w7Os14f0qv3",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"In a class, the implicit behavior of passing the object as the first argument is avoided if a method is declared as static, as shown in the following example."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "CJc8OOIR0Uif",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"class A(object):\n",
"\n",
" @staticmethod\n",
" def stat_meth():\n",
" print(\"Look no self was passed\")\n",
"\n",
"a = A()\n",
"a.stat_meth()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "zmSZEpuUwZPm",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"#### Inheritance\n",
"\n",
"Inheritance is the capability of one class to derive or inherit the properties from another class. The benefits of inheritance are:\n",
"\n",
"* It represents real-world relationships well.\n",
"* It provides reusability of a code. We don’t have to write the same code again and again. Also, it allows us to add more features to a class without modifying it.\n",
"* It is transitive in nature, which means that if class B inherits from another class A, then all the subclasses of B would automatically inherit from class A."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "8qnI09X2vpw8",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Inherited or Subclass (Note Person in bracket) \n",
"class Employee(Person): \n",
" \n",
" # Constructor\n",
" def __init__(self, name, year):\n",
" self.years = year # Create an instance variable\n",
" super().__init__(name)\n",
"\n",
" # Overriding Methods from the Parent Class\n",
" def isEmployee(self): \n",
" return True\n",
" \n",
"# Driver code \n",
"emp = Person(\"Geek1\") # An Object of Person \n",
"print(emp.getName(), emp.isEmployee()) \n",
" \n",
"emp = Employee(\"Geek2\", 20) # An Object of Employee \n",
"print(emp.getName(), emp.isEmployee()) "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "BUUw6EO1Y_zG",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"### Iterators"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "sJRb8KpFY_zI",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"source": [
"#### An iterator is an object that can be iterated upon, meaning that you can traverse through all the values."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "lv2d_g5tY_zJ",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"mytuple = (\"apple\", \"banana\", \"cherry\")\n",
"myit = iter(mytuple) # define\n",
"\n",
"print(next(myit)) # apple\n",
"print(next(myit)) # banana\n",
"print(next(myit)) # cherry\n",
"# Try this (uncomment)\n",
"# print(next(myit)) # raises StopIteration exception (not all exceptions are errors)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "E9gzSlmbY_zP",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"#### Strings, lists, tuples, dictionaries, and sets are all iterable objects."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "85n-oj49Y_zQ",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"mystr = \"banana\"\n",
"myit = iter(mystr)\n",
"\n",
"print(next(myit))\n",
"print(next(myit))\n",
"print(next(myit))\n",
"print(next(myit))\n",
"print(next(myit))\n",
"print(next(myit))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "eYfmOJZEY_zU"
},
"source": [
"#### Looping Through an Iterator"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "Kj14kEvZY_zU"
},
"source": [
"C-style approach"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "6gnYMQG4Y_zV"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"mytuple = (\"apple\", \"banana\", \"cherry\")\n",
"i = 0\n",
"while (i < len(mytuple)): \n",
" print(mytuple[i])\n",
" i += 1"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "FYkBGJ37Y_zZ",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"A better approach"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "shCmE0HNY_zb",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"mytuple = (\"apple\", \"banana\", \"cherry\")\n",
"\n",
"print(mytuple)\n",
"\n",
"for idx, val in enumerate(mytuple):\n",
" print(idx, val)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "h-rgh8adL8LK",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"mytuple = (\"apple\", \"banana\", \"cherry\")\n",
"\n",
"print(mytuple)\n",
"\n",
"for val in mytuple:\n",
" print(val)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "dUITksMsY_ze"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"mystr = \"banana\"\n",
"\n",
"for x in mystr:\n",
" print(x)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "LLO7jfIIY_zh"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Iterating over dictionary \n",
"d = dict() \n",
"d['xyz'] = 123\n",
"d['abc'] = 345\n",
"for i in d : \n",
" # print(\"%s %d\" %(i, d[i]))\n",
" print(\"{}\\t{}\".format(i, d[i]))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "6tDkn1koY_zj",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"#### Create an Iterator\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "jHEapd37Y_zk",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"source": [
"To create an object/class as an iterator, you have to implement the methods \\_\\_iter\\_\\_() and \\_\\_next\\_\\_() to your object.\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"* **\\_\\_iter\\_\\_** method that is called on initialization of an iterator. This should return an object that has a \\_\\_next\\_\\_ method.\n",
"* **\\_\\_next\\_\\_** should return the next value for the iterable. This method should raise a **StopIteration** to signal the end of the iteration.\n",
"\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "60grpN8LY_zk",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"class MyNumbers:\n",
" def __iter__(self):\n",
" self.a = 1\n",
" return self\n",
"\n",
" def __next__(self):\n",
" x = self.a\n",
" self.a += 1\n",
" return x\n",
"\n",
"myinstance = MyNumbers()\n",
"myiter = iter(myinstance)\n",
"\n",
"print(next(myiter))\n",
"print(next(myiter))\n",
"print(next(myiter))\n",
"print(next(myiter))\n",
"print(next(myiter))\n",
"\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "MJZGzf9IY_zn",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"Stop after 10 iterations by raising the StopIteration exception"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "xkWpi_H_Y_zo",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"class MyNumbers:\n",
" def __iter__(self):\n",
" self.a = 1\n",
" return self\n",
"\n",
" def __next__(self):\n",
" if self.a <= 10:\n",
" x = self.a\n",
" self.a += 1\n",
" return x\n",
" else:\n",
" raise StopIteration\n",
"\n",
"myclass = MyNumbers()\n",
"myiter = iter(myclass)\n",
"\n",
"for x in myiter:\n",
" print(x)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "yEGblopEY_zq"
},
"source": [
"#### zip function\n",
"Combine mulitple iterator"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "UsumWzQJY_zr"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Two separate lists \n",
"thing = [\"Apple\", \"Audi\", \"Pasta\", \"dog\", \"UMAINE\"] \n",
"category = [\"fruit\", \"car\", \"food\", \"animal\"] \n",
" \n",
"# Combining lists and printing \n",
"for t, c in zip(thing, category): \n",
" print(\"{} is {}\".format(t, c))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "8FN4iCf3Y_zx"
},
"source": [
"Use \"*\" operator to unzip"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "QI75XXjIY_zx"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"l1,l2 = zip(*[('Apple', 'fruit'), \n",
" ('Audi', 'car'), \n",
" ('Pasta', 'food') \n",
" ]) \n",
" \n",
"# Printing unzipped lists \n",
"print(l1) \n",
"print(l2) "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "6wqnuO2uY_z1",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"## yield vs return"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "kcQwfXs3_JA_",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"source": [
"Unlike normal functions that return a value and exit, **generator functions** automatically\n",
"suspend and resume their execution and state around the point of value generation.\n",
"Because of that, they are often a useful alternative to both computing an entire series\n",
"of values up front and manually saving and restoring state in classes. Because the state\n",
"that generator functions retain when they are suspended includes their entire local\n",
"scope, their local variables retain information and make it available when the functions\n",
"are resumed.\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"The chief code difference between generator and normal functions is that a generator\n",
"**yields** a value, rather than returning one—the yield statement suspends the function\n",
"and sends a value back to the caller, but retains enough state to enable the function to\n",
"resume from where it left off. When resumed, the function continues execution immediately\n",
"after the last yield run. From the function’s perspective, this allows its code\n",
"to produce a series of values over time, rather than computing them all at once and\n",
"sending them back in something like a list."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "dcU7dFMnY_z2",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"def simpleGeneratorFun(): \n",
" x = 5\n",
" # print(x)\n",
" yield 1 + x\n",
"\n",
" x = 2*x\n",
" #print(x)\n",
" yield 1 + x\n",
"\n",
" \n",
" x = 2*x\n",
" #print(x)\n",
" yield 1 + x"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "mxrp3zwE-nmI",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"simpleGeneratorFun()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "j0yItSVhAF3j",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"the next(X) built-in calls an object’s\n",
"`X.__next__()` method for us:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "ORAXLOxG_sOR",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"x = simpleGeneratorFun()\n",
"next(x)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "aY3m0CwoN0ym",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"list(simpleGeneratorFun())"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "QLV9WZDSNyh6",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Driver code to check above generator function \n",
"# simpleGeneratorFun()\n",
"list(simpleGeneratorFun())\n",
"\n",
"#for value in simpleGeneratorFun(): \n",
"# print(value) "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "gHaXG1EHY_z5",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"Yield are used in Python generators. A generator function is defined like a normal function, but whenever it needs to generate a value, it does so with the yield keyword rather than return. If the body of a def contains yield, the function automatically becomes a generator function."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "C7j8oMVIY_z5",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"def nextSquare(): \n",
" i = 1; \n",
" \n",
" # An Infinite loop to generate squares \n",
" while True: \n",
" yield i*i \n",
" i += 1 # Next execution resumes \n",
" # from this point \n",
" \n",
"# Driver code to test above generator \n",
"# function \n",
"for num in nextSquare(): \n",
" if num > 100: \n",
" break \n",
" print(num) "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "a60k2X4QY_z8",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"## Modules and Packages"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "D0szgI5ZY_z_",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Packages are stored on PyPi servers by default and can be directly installed from github as well.\n",
"!pip install --user import-ipynb"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "7U66Oi23Y_0D",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import import_ipynb\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"%%writefile myModule.py\n",
"\n",
"s = \"hi from my module\""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"source": [
"Every python file is a module and can be imported. import executes everything in the module."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"deletable": false,
"nbgrader": {
"cell_type": "code",
"checksum": "ed3306295ddc8cae2191697d284965a8",
"grade": true,
"grade_id": "cell-5b99e5e743718896",
"locked": false,
"points": 10,
"schema_version": 3,
"solution": true,
"task": false
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
},
"tags": []
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# YOUR CODE HERE\n",
"raise NotImplementedError()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "W3v5ddVBY_0J",
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import sys\n",
"import os\n",
"\n",
"dirpath = os.getcwd()\n",
"print(\"current directory is : \" + dirpath)\n",
"foldername = os.path.basename(dirpath)\n",
"print(\"Directory name is : \" + foldername)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"You can create nested modules by directory structure:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"!mkdir -p my_module"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"source": [
"You can not import an empty directory. You have to drop (maybe empty) `__init__.py` in the directory."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "fragment"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"%%writefile my_module/__init__.py\n",
"\"\"\" My module is the best module ever. \"\"\"\n",
"def identity(x):\n",
" \"\"\" This function always returns what it is given \"\"\"\n",
" return x\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"Now you can import my_module."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import my_module\n",
"help(my_module)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"You can move python files into hierarchies and directories."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"!cp myModule.py my_module"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "-"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import my_module.myModule as mmmm\n",
"mmmm.s"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "slide"
}
},
"source": [
"## Read More\n",
"\n",
"1. [List of all Python Keywords](https://docs.python.org/3/reference/lexical_analysis.html#keywords)\n",
"\n",
" False await else import pass\n",
" None break except in raise\n",
" True class finally is return\n",
" and continue for lambda try\n",
" as def from nonlocal while\n",
" assert del global not with\n",
" async elif if or yield\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"2. [List of all Python builtins](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#built-in-funcs)\n",
"\n",
"3. [List of all Python operators and their precedence](https://docs.python.org/3/reference/expressions.html?highlight=bitwise%20operators#operator-precedence)"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"accelerator": "TPU",
"colab": {
"private_outputs": true,
"provenance": [],
"toc_visible": true
},
"gpuClass": "standard",
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.9.13"
},
"rise": {
"enable_chalkboard": true,
"theme": "serif"
},
"toc-autonumbering": true,
"toc-showcode": false,
"toc-showmarkdowntxt": false
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 4
}